Mercury(II) Acetate
Product Details:
- Purity 98% min
- Melting Point 178 C
- Smell Odorless
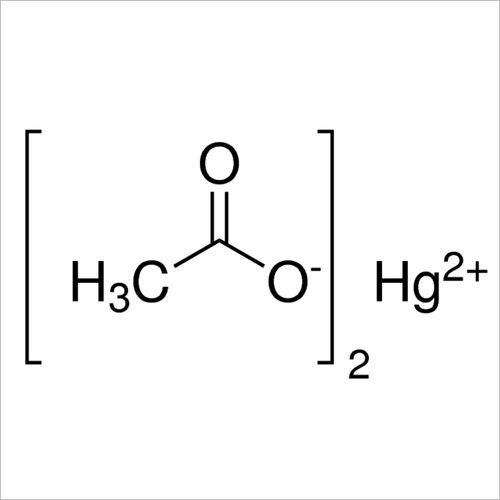
- Structural Formula (CH3COO)2Hg
- Poisonous Yes
- Boiling point Decomposes before boiling
- Appearance White crystalline powder
- Click to View more
Mercury(II) Acetate Price And Quantity
Mercury(II) Acetate Product Specifications
- 28439090
- (CH3COO)2Hg
- Yes
- Mercuric Acetate; Acetic acid, mercury(2+) salt
- Odorless
- 178 C
- 98% min
- Odorless
- Soluble in water, alcohol, and ether
- Crystalline
- 318.68 g/mol
- Analytical Reagent (AR), Laboratory Grade
- Neutral to slightly acidic
- C4H6HgO4
- 216-465-3
- 3.28 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- White crystalline powder
- 1600-27-7
- Solid
- Decomposes before boiling
Product Description
Mercury (II) acetate is mainly suited for mercuration of different organic compounds. It allows for the absorption of ethylene. This is a chemical midway for phenylmercuric acetate. It is also compatible with organomercury compounds. Offered is functional as a catalyst in organic synthesis and assists in the manufacturing of several pharmaceuticals. Mercury (II) acetate is popular as a reagent which can make several organomercury compounds. Also, this is used to remove the acetamidomethyl protecting group. This is slightly soluble with alcohols, insoluble with hexane & benzene and highly soluble with water (H2O).
Specification
| Purity | Min.97% |
| Grade | LR/AR |
| Packaging Type | JAR/DRUM |
| Packaging Size | 500GM/25KG |
| Chemical Formula | (CH3COO)2Hg |
| CAS Number | 1600-27-7 |
| Molecular Weight | 318.68 |
Exceptional Purity for Reliable Results
As an Analytical Reagent (AR) grade compound, mercury(II) acetate ensures high purity (minimum 98%), fostering reproducible outcomes in research and industrial processes. Its white crystalline form and solubility in water, alcohol, and ether make it suitable for a broad spectrum of chemical applications.
Stringent Safety and Storage Protocols
To retain stability, store mercury(II) acetate in sealed HDPE bottles or glass containers, away from light and moisture. Adhere strictly to recommended handling precautions, including the use of gloves and eye protection, as it is highly toxic. Strictly avoid contact with strong reducing agents, ammonia, and sulfur compounds.
Versatile Functions and Applications
Mercury(II) acetate serves as a reagent, catalyst, and mediator in organic synthesis and analytical chemistry. Its stability and neutral to slightly acidic pH facilitate diverse reactions, making it essential for laboratories, exporters, and manufacturers seeking high-performance chemicals.
FAQs of Mercury(II) Acetate:
Q: Where should I store mercury(II) acetate to maintain its stability?
A: Mercury(II) acetate should be kept in a tightly closed HDPE bottle or glass container, protected from light and moisture. Proper storage ensures stability and prolongs its shelf life to two years.Q: What are the recommended handling precautions for this compound?
A: When working with mercury(II) acetate, always use gloves and eye protection. Avoid inhalation and direct contact with skin to minimize health risks due to its toxic nature.Q: How is mercury(II) acetate typically used in laboratories?
A: This compound finds essential use as a reagent and catalyst in organic synthesis, analytical chemistry, and a variety of chemical processes requiring its specific reactivity and solubility.Q: What should I avoid combining with mercury(II) acetate during experiments?
A: Mercury(II) acetate must not be mixed or stored with strong reducing agents, ammonia, or sulfur compounds, as these can cause incompatibility issues and potentially harmful reactions.Q: When does mercury(II) acetate decompose and what are the implications?
A: Mercury(II) acetate decomposes upon heating and does not have a boiling point; always conduct experiments at safe temperatures and avoid exposing the compound to heat to prevent hazardous conditions.Q: What are the benefits of using mercury(II) acetate in organic synthesis?
A: Mercury(II) acetate provides selectivity, efficiency, and reliability in chemical reactions, thanks to its purity and consistent analytical performance, contributing to precise results.
Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Other Products in 'Fine Chemicals' category
 |
SUVIDHINATH LABORATORIES
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |